Your medical history, as well as your typical voice habits, onset and progression of dysphonia, etc. are all very important information in determining a diagnosis and management plan for your dysphonia. Following a general otolaryngology examination, usually including fiberoptic endoscopic examination of the larynx, further stroboscopic evaluation of your dysphonia will typically be performed.
Stroboscopy
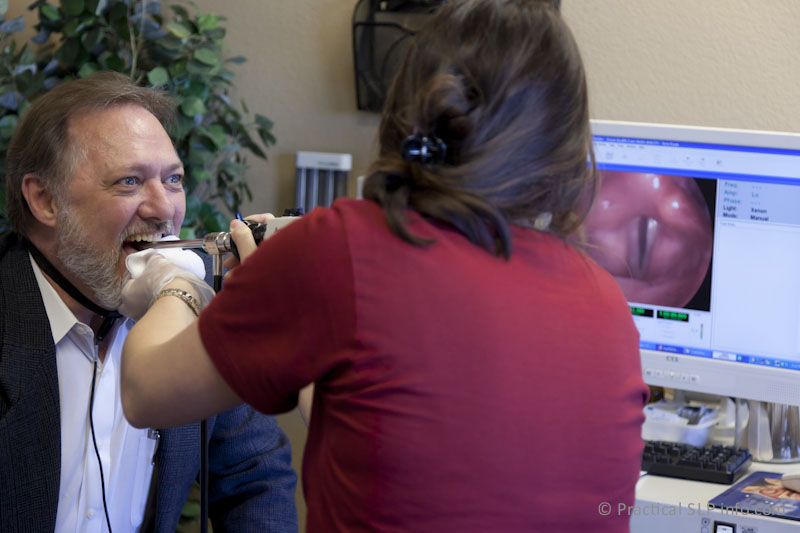
Stroboscopic examination is key to establishing the etiology, or cause, of the voice disorder, which then allows for proper management. Although your doctor may have used a flexible fiberscope (through the nose) to examine your larynx, stroboscopy offers a higher level of examination when there is concern regarding the voice and/or the general health of the larynx.
For this examination, a microphone resembling the end of a stethoscope will be secured around your neck. A rigid endoscope is then placed into the mouth and passed to the back of the throat. A lens at the end of the scope allows for a magnified examination of the larynx, beyond what is possible with the flexible fiberscopes used in this office.
Once the scope is in position to view the larynx, you will be asked to produce the sound “eeeeeee.” During this time, a strobe light will allow for visualization of the actual vocal cord vibrations. It is the use of the strobe light that makes this examination different from other endoscopic examinations. The vocal cords vibrate at a very high speed, making it impossible to observe the vibrations with the naked eye.
Consider watching a hummingbird’s wings while it is hovering. Although it is clear the wings are moving, they are doing so too quickly to see with any clarity. The same is true of the vocal cords during phonation. Being able to see these vibrations through the use of stroboscopy allows for a comprehensive examination of your phonatory pattern.
VOcal Parameters
The larynx is capable of producing a voice in many different ways. For example, you can speak softly, shout, sing and laugh. For this reason, when assessing voice disorders, it is important to also see what the larynx is capable of doing. Identifying areas that are not considered to be “normal” can be very important in determining a proper diagnosis and management plan. Measuring change and/or improvement in these areas is also helpful in determining the success of treatment.
As part of your voice evaluation, you may be asked to perform certain tasks during which the SLP staff will be taking measurements and making observations. These will include your typical speaking frequency (pitch), how much you can vary the pitch of your voice, how loud you can be, how long you can sustain a voice, etc. All of this information can be very helpful in assessing your dysphonia, determining proper treatment and then tracking change/improvement based upon those initial measurements.