Candida is a fungus that lives naturally in the human body. This fungus lives in warm, moist and dark places that typically have very little exposure to light. In certain circumstances, candida will flourish in a specific area, causing an infection. This is the case when “thrush” occurs in the mouth or throat. Thrush is a common name used to describe a candida infection in these areas.
This same fungus will typically grow on the surfaces of the voice prosthesis. It is this growth that accounts for the most common cause of valve failure, when there is persistent leakage that cannot be controlled by typical cleaning and/or troubleshooting methods.
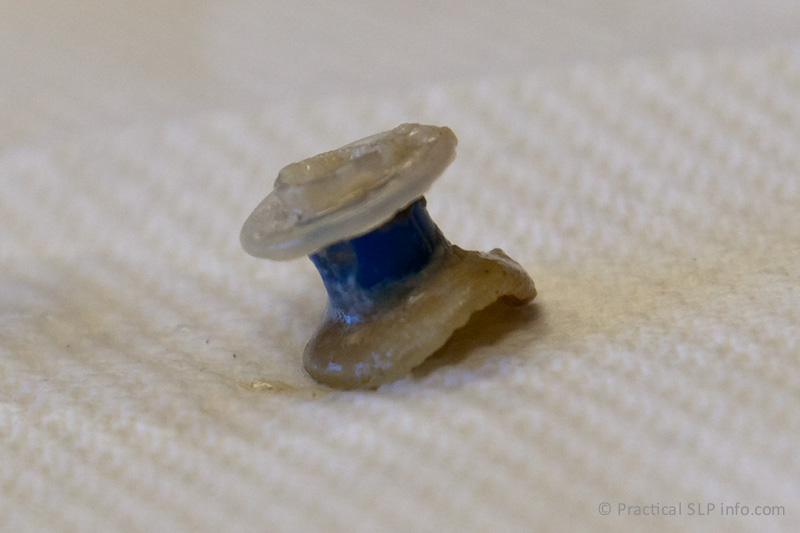
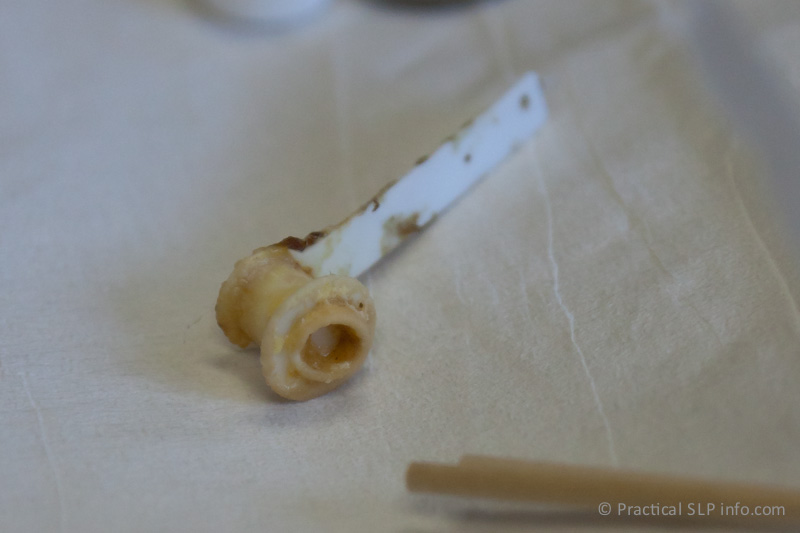
When candida colonizes on the voice prosthesis, it may grow in an area that interferes with proper valve closure. In essence, the candida growth causes the valve to be “propped open,” allowing liquids and saliva to pass into the lumen of the voice prosthesis and potentially leaking into the trachea. See some photographs of fungus on a voice prosthesis.
This same fungus will typically grow on the surfaces of the voice prosthesis. It is this growth that accounts for the most common cause of valve failure, when there is persistent leakage that cannot be controlled by typical cleaning and/or troubleshooting methods.
When candida colonizes on the voice prosthesis, it may grow in an area that interferes with proper valve closure. In essence, the candida growth causes the valve to be “propped open,” allowing liquids and saliva to pass into the lumen of the voice prosthesis and potentially leaking into the trachea. See some photographs of fungus on a voice prosthesis.
Although candida is a naturally occurring fungus, how much it is allowed to grow varies widely from person to person. Individual patients may also notice changes in how quickly they do/do not experience candida growth. Changes in body chemistry (hormonal changes), diet, and certain medications are known to impact candida growth. Many patients do not experience any difficulty at all with fungal growth beyond what is considered to be “normal.” Should the SLP staff determine you are experiencing particularly short prosthesis lifetimes (i.e., the voice prosthesis is being replaced frequently), and determine this is due to excessive candida growth on the prosthesis, you may be instructed/prescribed a particular regimen to help control fungal growth and improve the lifetime of your voice prosthesis. In doing so, you may be able to extent the time between changes.
There are various anti-fungal agents/medications that can be prescribed to you if deemed appropriate. The following are the most-commonly prescribed agents as well as the typical instructions for use. It is important, however, to follow the guidelines prescribed to you by your doctor or SLP staff. It is always important that you regularly clean your prosthesis, with or without using any methods described below.
In general, yogurt is recommended to all patients. Eating yogurt regularly is believed to help significantly impact the growth of candida. Yogurt cultures are believed to inhibit fungal growth.
Coca-Cola (brand name, not generic) is also believed to be effective against candida growth. Drinking one can per day may be helpful in preventing fungal growth on the prosthesis.
The following are prescription medications commonly used by this practice to assist with controlling fungal growth that appears to be more aggressive. Your doctor or SLP staff will determine if these are appropriate, as well as indicate appropriate use:
Nystatin (Suspension): This is a liquid medication that works by treating the fungus in a topical manner. In order to be effective, the medicine must come in direct contact with the fungus. For an oral/throat infection, you may be instructed to swish this medicine in your mouth for several seconds, then swallow.
For candida prophylaxis (prevention) with regard to the voice prosthesis, we recommend using your brush with the Nystatin.
Before using this, be sure you have thoroughly cleaned your prosthesis with the brush/flush. Once the prosthesis has been cleaned, dip the clean brush into the Nystatin and insert into the prosthesis as if you were cleaning, rotating the brush in place to ensure adequate contact with the device. This may be repeated. Rinse the medication from the brush and allow the brush to air dry as usual.
NOTE: Some patients report Nystatin use with the brush may cause the valve to stick slightly. In this case, wait 10 minutes after using the Nystatin on the brush, then clean your prosthesis as usual.
Diflucan (Fluconazole): This is a systemic medication, working internally to assist in reducing the fungal count in your entire body and most commonly prescribed in the event of an active infection. This may be prescribed alone or used in combination with Nystatin. This is typically a once-daily pill, which can be taken by mouth or put through a g-tube. It is important you finish the entire course of medication, similar to finishing an antibiotic.
There are various anti-fungal agents/medications that can be prescribed to you if deemed appropriate. The following are the most-commonly prescribed agents as well as the typical instructions for use. It is important, however, to follow the guidelines prescribed to you by your doctor or SLP staff. It is always important that you regularly clean your prosthesis, with or without using any methods described below.
In general, yogurt is recommended to all patients. Eating yogurt regularly is believed to help significantly impact the growth of candida. Yogurt cultures are believed to inhibit fungal growth.
Coca-Cola (brand name, not generic) is also believed to be effective against candida growth. Drinking one can per day may be helpful in preventing fungal growth on the prosthesis.
The following are prescription medications commonly used by this practice to assist with controlling fungal growth that appears to be more aggressive. Your doctor or SLP staff will determine if these are appropriate, as well as indicate appropriate use:
Nystatin (Suspension): This is a liquid medication that works by treating the fungus in a topical manner. In order to be effective, the medicine must come in direct contact with the fungus. For an oral/throat infection, you may be instructed to swish this medicine in your mouth for several seconds, then swallow.
For candida prophylaxis (prevention) with regard to the voice prosthesis, we recommend using your brush with the Nystatin.
Before using this, be sure you have thoroughly cleaned your prosthesis with the brush/flush. Once the prosthesis has been cleaned, dip the clean brush into the Nystatin and insert into the prosthesis as if you were cleaning, rotating the brush in place to ensure adequate contact with the device. This may be repeated. Rinse the medication from the brush and allow the brush to air dry as usual.
NOTE: Some patients report Nystatin use with the brush may cause the valve to stick slightly. In this case, wait 10 minutes after using the Nystatin on the brush, then clean your prosthesis as usual.
Diflucan (Fluconazole): This is a systemic medication, working internally to assist in reducing the fungal count in your entire body and most commonly prescribed in the event of an active infection. This may be prescribed alone or used in combination with Nystatin. This is typically a once-daily pill, which can be taken by mouth or put through a g-tube. It is important you finish the entire course of medication, similar to finishing an antibiotic.